Shipping goods isn't just about moving boxes—it’s about aligning logistics with your business goals. Delivery freight shipping encompasses a range of methods to transport goods, from raw materials to finished products. But how do you select the best approach? Let’s explore the key factors that define successful freight delivery.
What Is Delivery Freight Shipping?
Delivery freight shipping refers to the end-to-end process of transporting goods from suppliers to end customers or distribution centers. Unlike last-mile delivery (which focuses on the final leg), freight shipping covers the entire journey, often involving multiple modes like sea, air, rail, or road.
Key components include:
- Mode Selection: Balancing speed, cost, and cargo type.
- Documentation: Bills of lading, customs forms, and insurance.
- Risk Management: Mitigating delays, damage, or loss.
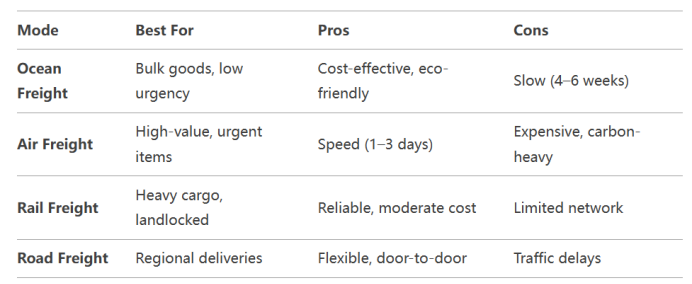
Comparing Freight Shipping Modes
Each transportation method has trade-offs:
4 Steps to Optimize Freight Shipping
1. Categorize Your Cargo
- Perishables (food, flowers): Prioritize speed and temperature control.
- Fragile items (electronics): Opt for secure handling and shockproof packaging.
- Non-urgent bulk (textiles): Choose cost-efficient modes like sea or rail.
2. Map Your Supply Chain
Identify bottlenecks: Are customs delays eating into air freight’s speed advantage? Could a regional warehouse reduce dependency on long-haul shipping?
3. Leverage Hybrid Solutions
Example: Ship bulk components via sea, then use road freight for just-in-time assembly line deliveries.
4. Implement Tracking Systems
GPS-enabled IoT devices provide real-time location updates, while blockchain platforms enhance document security.
Hidden Costs (and How to Avoid Them)
- Dimensional Weight Pricing: Carriers charge by size, not just weight. Optimize packaging to avoid "empty space" fees.
- Detention Charges: Late container returns at ports incur penalties. Schedule pickups/drop-offs meticulously.
- Emergency Rerouting: Fuel surcharges spike during geopolitical crises. Build contingency budgets.
Sustainability in Freight Shipping
- Route Optimization: AI tools identify fuel-efficient paths, reducing emissions.
- Intermodal Shipping: Combining rail and road cuts carbon footprints by 30% vs. truck-only.
- Eco-Packaging: Reusable crates or biodegradable materials minimize waste.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Overlooking Insurance: A single damaged pallet can outweigh annual insurance costs.
- Fragmented Carriers: Using multiple vendors without integration causes tracking chaos.
- Static Strategies: Re-evaluate shipping methods quarterly as fuel costs and regulations shift.
The Future of Freight Shipping
1. Autonomous Trucks: Piloted in controlled environments for long-haul routes.
2. Digital Freight Marketplaces: Instant rate comparisons across carriers.
3. Green Corridors: Governments subsidize low-emission shipping lanes.
Final Checklist
- Audit shipping contracts annually for hidden fees.
- Train staff on Incoterms (e.g., FOB vs. CIF) to avoid liability gaps.
- Partner with carriers offering transparent analytics dashboards.
Delivery freight shipping isn't one-size-fits-all. By matching strategies to cargo needs, businesses can achieve reliability, cost control, and sustainability—all at once.






